Topology-Preserving Segmentation Network: A Deep Learning Segmentation Framework for Connected Component
Abstract
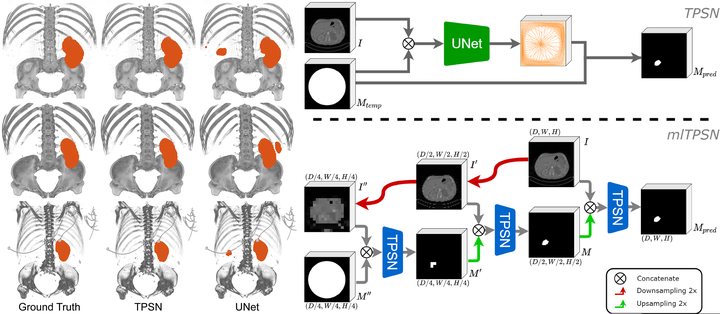
Medical image segmentation, which aims to automatically extract anatomical or pathological structures, plays a key role in computer-aided diagnosis and disease analysis. Despite the problem has been widely studied, existing methods are prone to topological errors. In medical imaging, the topology of the structure, such as the kidney or lung, is usually known. Preserving the topology of the structure in the segmentation process is of utmost importance for accurate image analysis. In this work, a novel learning-based segmentation model is proposed. A topology-preserving segmentation network (TPSN) is trained to give an accurate segmentation result of an input image that preserves the prescribed topology. TPSN is a deformation-based model that yields a deformation map through a UNet, which takes the medical image and a template mask as inputs. The main idea is to deform a template mask describing the prescribed topology by a diffeomorphism to segment the object in the image. The topology of the shape in the template mask is well preserved under the diffeomorphic map. The diffeomorphic property of the map is controlled by introducing a regularization term related to the Jacobian in the loss function. As such, a topology-preserving segmentation result can be guaranteed. Furthermore, a multi-scale TPSN is developed in this paper that incorporates multi-level information of images to produce more precise segmentation results. To evaluate our method, we applied the 2D TPSN on Ham10000 and 3D TPSN on KiTS21. Experimental results illustrate our method outperforms the baseline UNet segmentation model with/without connected-component analysis (CCA) by both the dice score and IoU score. Besides, results show that our method can produce reliable results even in challenging cases, where pixel-wise segmentation models by UNet and CCA fail to obtain accurate results.